MEDI-K.O. on Twitter: "Perfect Competition Concepts & Graphs You Must Know - MR=MC Output, MR=D=AR=P, MC=S Above Min. AVC #apmicroeconomics http://t.co/OflsxNenoK" / Twitter

Characteristics of a Monopoly D=AR=P > MR Monopoly Profit Maximization Comparing Monopoly to Perfect Competition Monopoly: Inefficient?? Price Discrimination. - ppt download

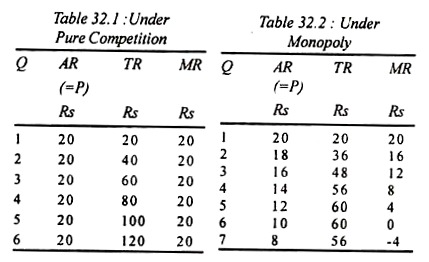
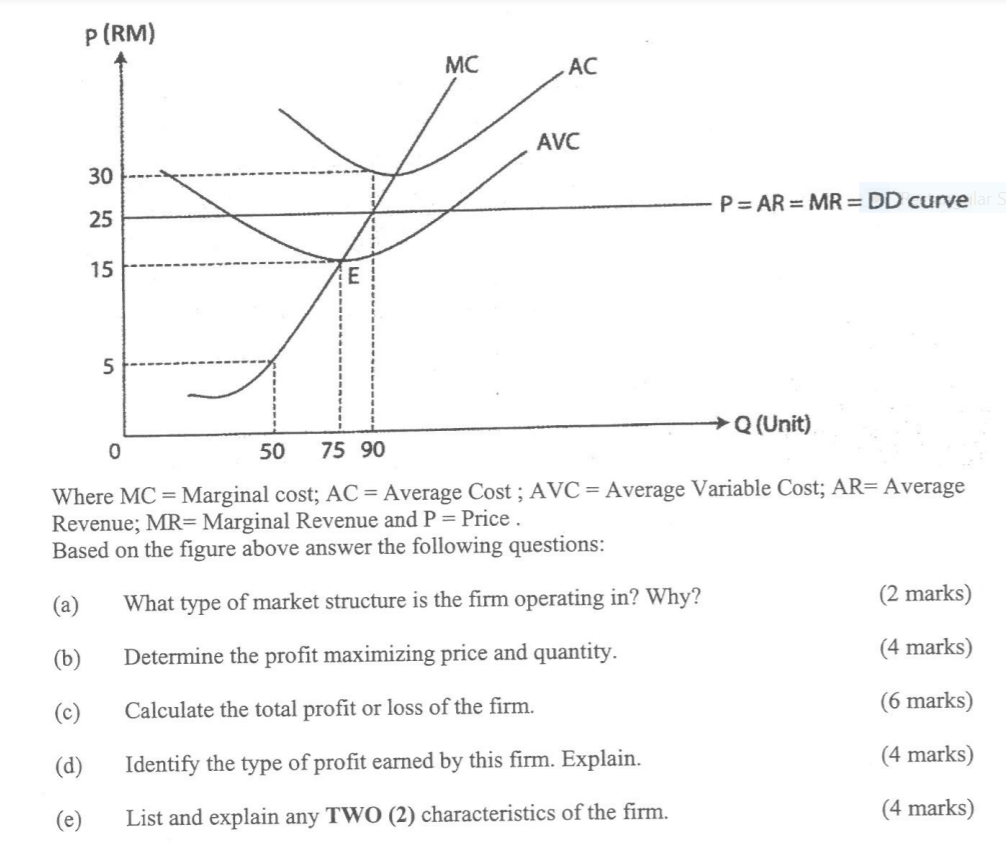
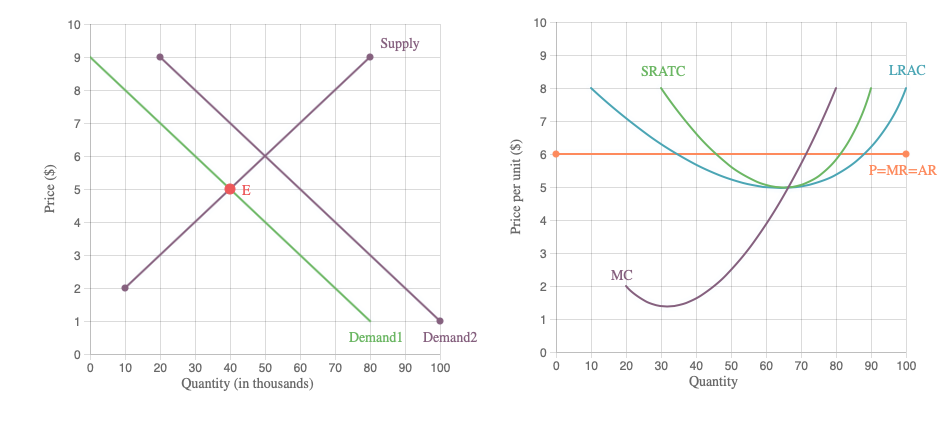
a. Compute MR, AR, AC, AFC, AVC, and MC. b. Draw a graph showing P, AR, MR, AVC, ATC, and MC, and then identify the profit maximum level of output. c. Draw

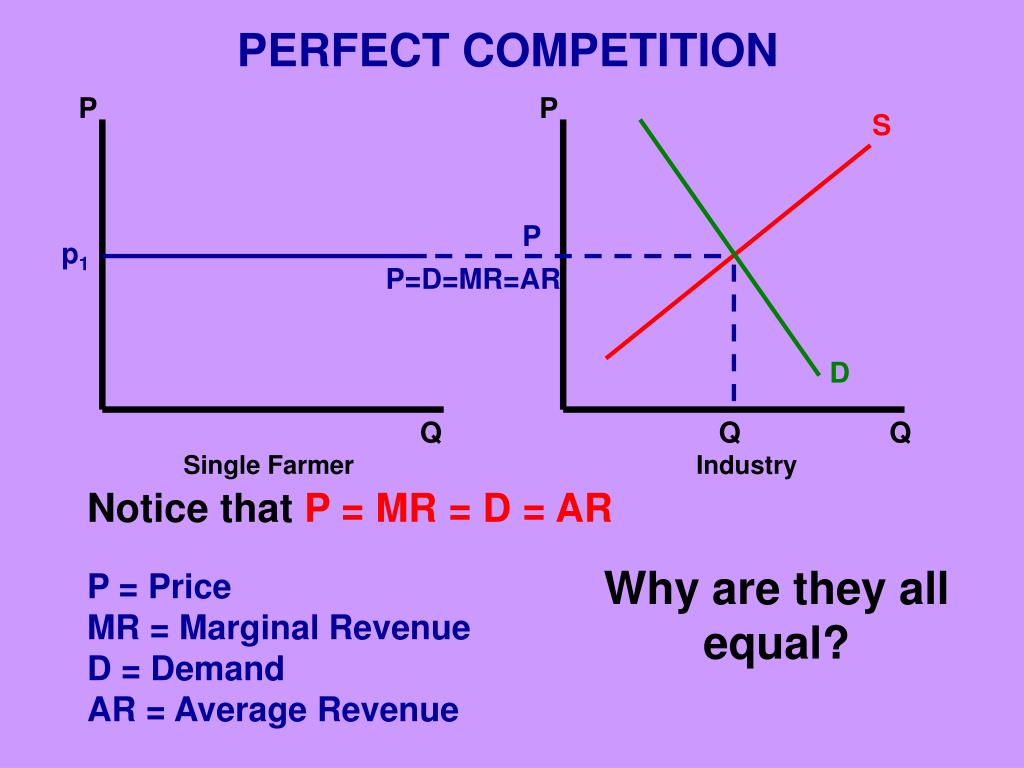
And Unit 3 – Theory of the FirmPart Many buyers and sellers 2. All the products are homogeneous. 3. All buyers & sellers are price takers. 4. There. - ppt download
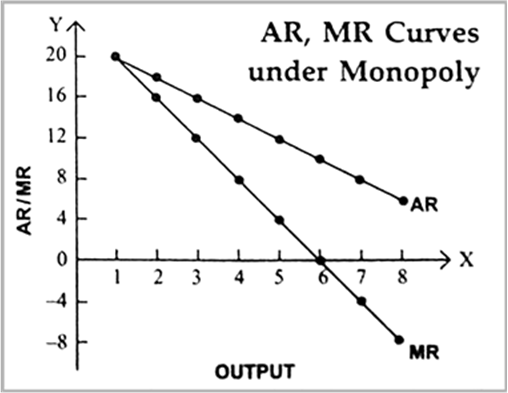
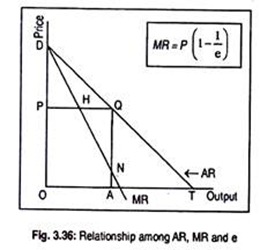
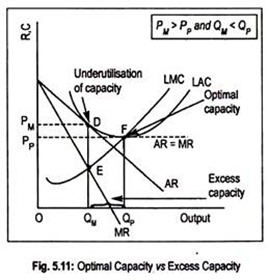
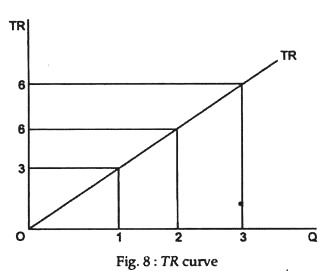
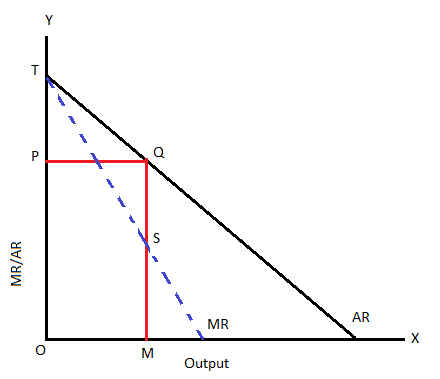
Under perfect competition MR = AR but under monopoly (or monopolistic condition) MR is less than AR (MR < AR). Explain. from Economics The Theory Of The Firm Under Perfect Competition Class 12 CBSE

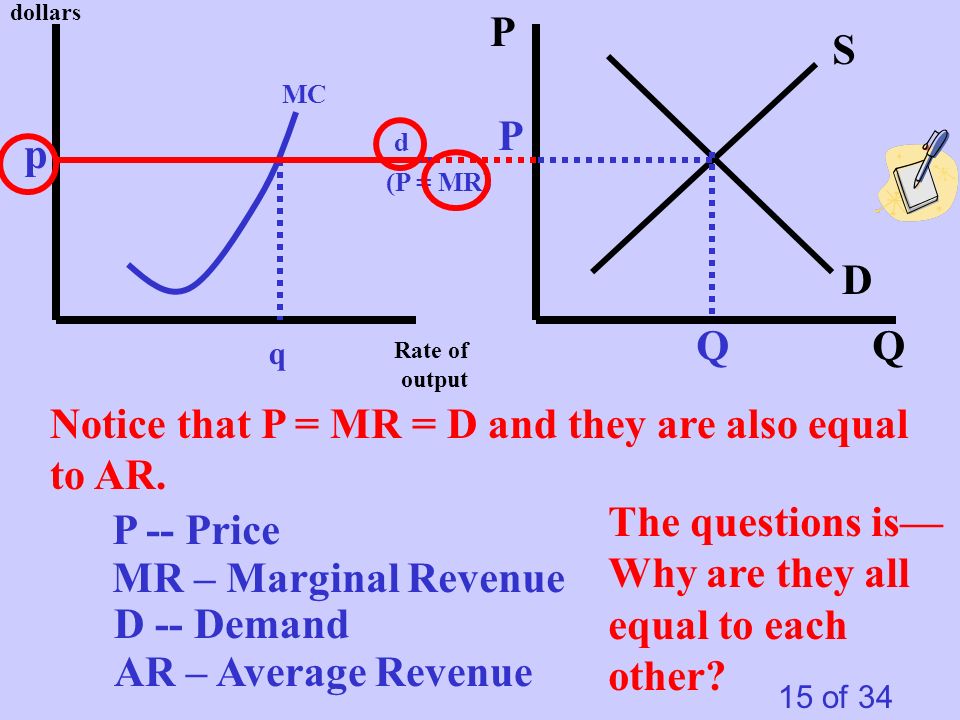
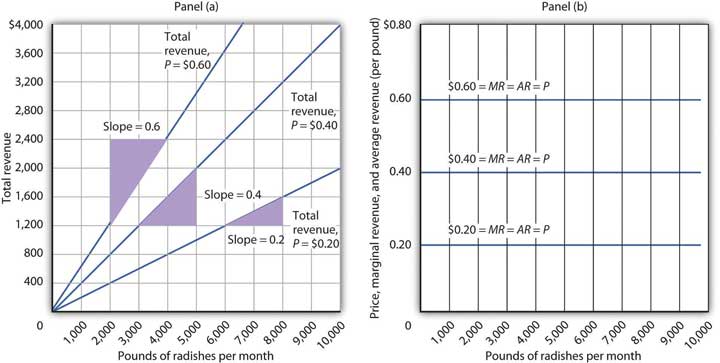
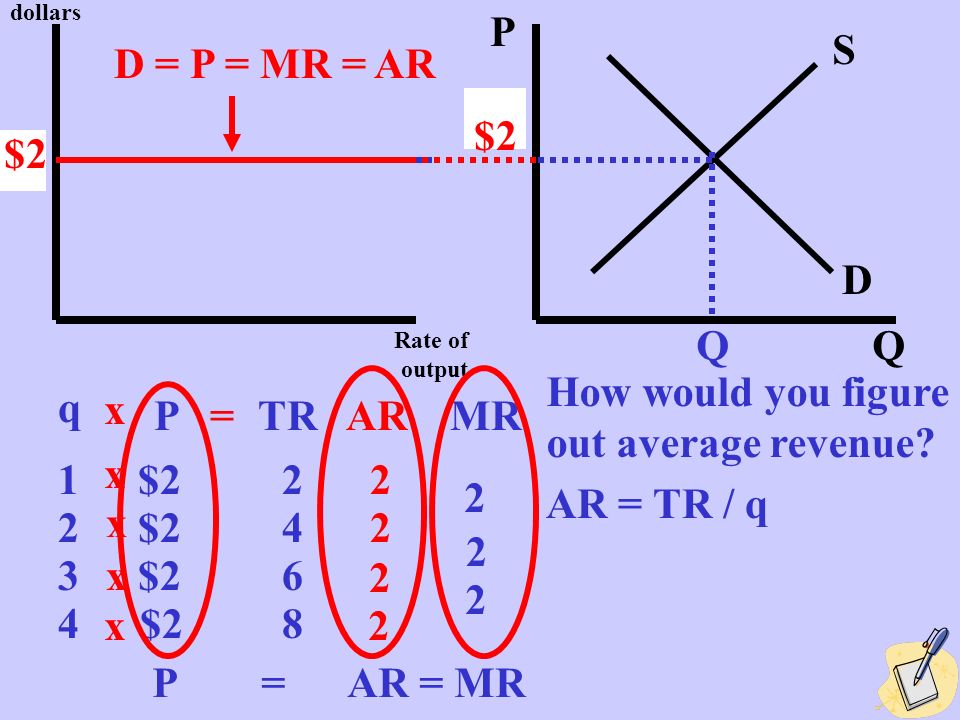
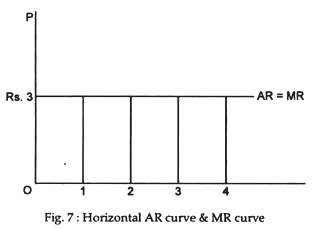
Shorts Prove that P=MR=AR=D :Price=marginal revenue= average revenue= demand in perfect competition - YouTube